G10 VQ Connecting Link

- Safety first! A connector that’s stiff or won’t move has likely been overloaded. Don’t use it – replace it.
Grade 100 Connecting Link, designed for maximum strength and durability in heavy lifting applications. Crafted from high-quality alloy steel, this connecting link ensures secure and efficient load handling.
- Forged specialty alloy steel, and then heat treated;
- Can be matched with G100 chains;
- Performance is increased by 25% compared with G80 products;
- Each Piece is tested at 2.5 times the working load limit;
- Fatigue testing is carried out on samples to 20,000 times;
- Strict sampling and breakage testing is conducted for each batch of products;
- 100% magnetic powder flaw detection is performed;
- 100% of the pins are tested to ensure they have the same hardness;
- Surface treatment: Powder Coated;
- Colour code: Peach and Black;
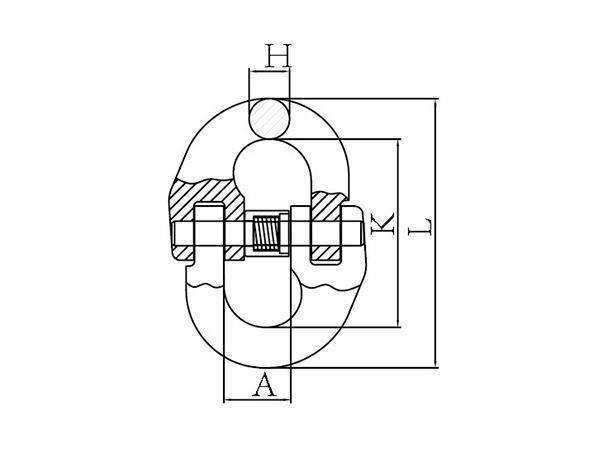
| Model | Part Number | WLL (t) | Breaking Load (t) | A±.1.5 | H±1 | K±2 | L±2.5 | Weight (KG) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10-VQCL1001-08 | 3956 5016 | 2.5 | 10 | 18.5 | 10 | 61.5 | 84.5 | .18 |
| 10-VQCL1001-10 | 3956 5024 | 4 | 16 | 23 | 12.6 | 72 | 97.2 | .34 |
| 10-VQCL1001-13 | 3956 5032 | 6.7 | 26.8 | 27.5 | 16.8 | 89 | 127 | .68 |
| 10-VQCL1001-16 | 3956 5040 | 10 | 48 | 33.5 | 21 | 103 | 145 | 1.22 |
| 10-VQCL1001-20 | 3956 5048 | 16 | 64 | 42 | 24.5 | 116 | 175 | 2.13 |
| 10-VQCL1001-22 | 3956-5056 | 19 | 76 | 48 | 27 | 135 | 193 | 3 |
Other Products
Inspection Considerations for G80 and G100 Alloy Connecting Link
Inspecting a Grade 80/100 connecting link involves several critical steps to ensure safety and compliance with industry standards. Here’s a comprehensive guide to help you perform this inspection:
Visual Inspection
Check for Identification: Ensure the connecting link has clear identification markings, including the grade, manufacturer’s mark, and traceability code. This is essential for verifying that the link meets Grade 100 specifications.
Examine for Deformation: Look for any signs of deformation, such as bends, twists, or elongation. Deformed links indicate that the link has been overloaded and should be removed from service.
Inspect for Wear: Check the connecting link for any signs of excessive wear, especially at the points where it connects to other components. Measure the dimensions of the worn areas and compare them to the original dimensions to determine if the wear exceeds acceptable limits.
Surface Defects: Look for cracks, gouges, nicks, and corrosion. Surface defects can compromise the integrity of the link and are often indicators of underlying problems.
Check for Heat Damage: Inspect for signs of heat exposure, such as discoloration, which can weaken the material. Grade 100 links are heat-treated, and exposure to high temperatures can alter their properties.
Functional Inspection
Movement of Components: Ensure that the connecting link’s components move freely without restriction. If the link is part of a more complex assembly, all parts should function together smoothly.
Fit and Alignment: Verify that the link fits correctly with the components it is designed to connect. Misalignment or improper fit can indicate wear or deformation.
Measurement and Comparison
Dimensional Check: Use calipers or other precise measuring tools to check the dimensions of the connecting link against the manufacturer’s specifications. Pay special attention to critical dimensions such as the thickness of the link and the diameter of any pins or bolts.
Reach Measurement: Measure the reach (the effective length) of the connecting link. If it exceeds the specified length, it may have been stretched and should be replaced.
Record Keeping
Documentation: Record all findings in an inspection log. Include the date of inspection, the condition of the link, any defects found, and the actions taken (such as removal from service).
Traceability: Maintain traceability records that link the connecting link to its inspection history. This is important for maintaining compliance with safety standards and for future reference.
Compliance Check
OSHA and Local Regulations: Ensure that the inspection complies with OSHA regulations and any local safety standards. This may include additional requirements for documentation, frequency of inspections, and criteria for removing links from service.
Manufacturer Guidelines: Follow the manufacturer’s inspection and maintenance guidelines. These often include specific criteria for wear and deformation that are unique to their products.
By performing these steps, you ensure that Grade 100 connecting links are safe for use and comply with all relevant standards and regulations. Regular inspections help prevent accidents and extend the life of your lifting equipment.
For more detailed guidelines, you can refer to resources such as:
- OSHA standards
- WorkSafeBC (WorkSafeBC) (WorkSafeBC)
- Manufacturer-specific guidelines from the product manual.
Always check your local laws and governing bodies in your region to ensure compliance with all relevant regulations and standards for chain sling inspections.
Accuracy Disclaimer: While we strive to provide accurate and up-to-date inspection information, please be aware that regulations, standards, and guidelines may change. It is important to verify the information provided by your local governing bodies or relevant authorities to ensure compliance with current regulations and requirements.